Path of REBUS Analysis
You can perform Path Analysis by the following path or REBUS button:
1- SEM-PLS
2- REBUS Analysis
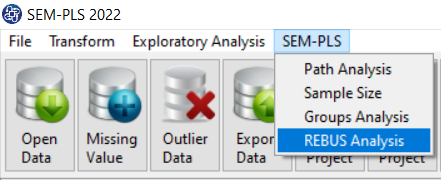
A. REBUS Analysis:
REBUS Analysis window includes five tabs: Latent Variables, Relations, Regression Methods, REBUS Tests, and REBUS Path Diagram.
The first three tabs are similar to “Path Analysis”. The user may use the software only for the REBUS Analysis.
For this purpose, three tabs in “Path Analysis” are listed in this window. Therefore, to REBUS Analysis,
there is no need to use the “Path Analysis” window.
Note that any changes in this window will apply to the SEM-PLS Model in other windows and conversely.
(See Path Analysis)
B. REBUS Tests:
B1. Method:
In this panel, you can select the REBUS tests in the following two methods:
1-t test
2- Permutation test
(See
Introduction to SEM-PLS: E.4.3. REBUS (Response Based Unit Segmentation)
)
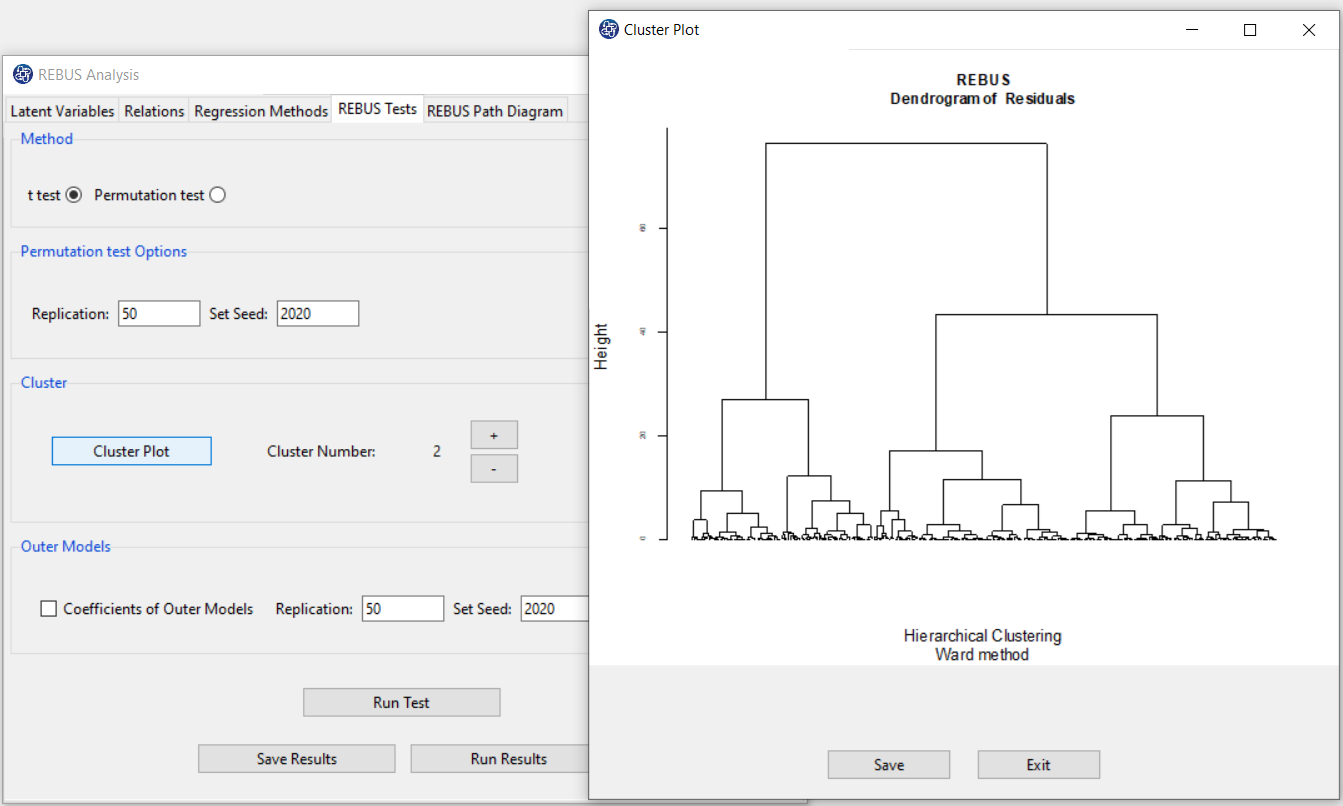
B2. Cluster:
Based on “Cluster Plot”, you can determine the “Cluster Number” that you want to perform this analysis.
You can increase or decrease the number of clusters with the + or - buttons, respectively.
Similarly, this panel is repeated in “REBUS Path Diagram” tab.
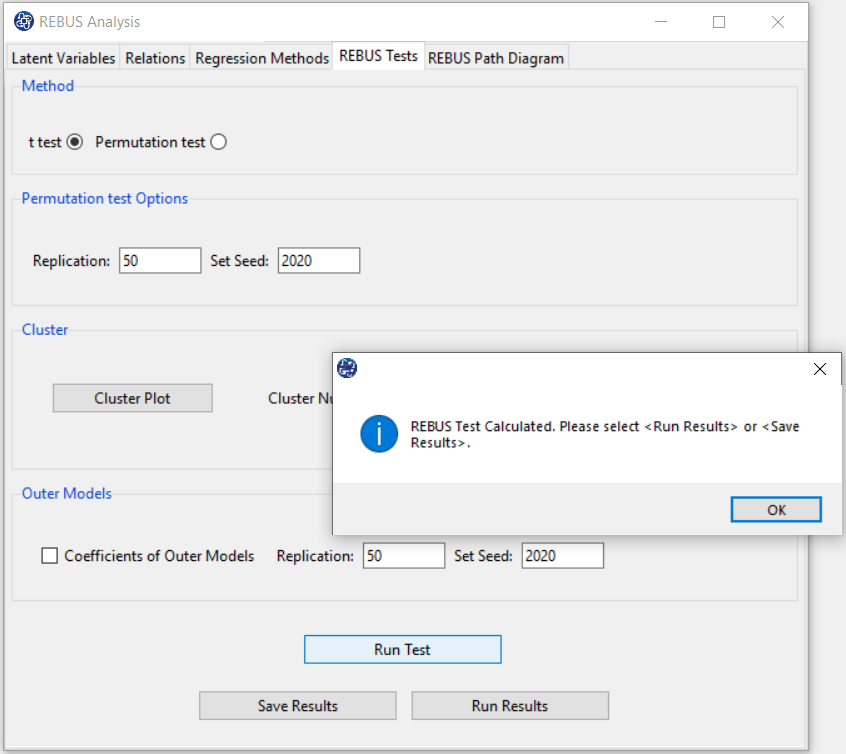
B3. Run Test:
By clicking this button, you can REBUS Test.
If this test is done without problems, this message appears:
“REBUS Test Calculated. Please < Run Results> or < Save Results>.“
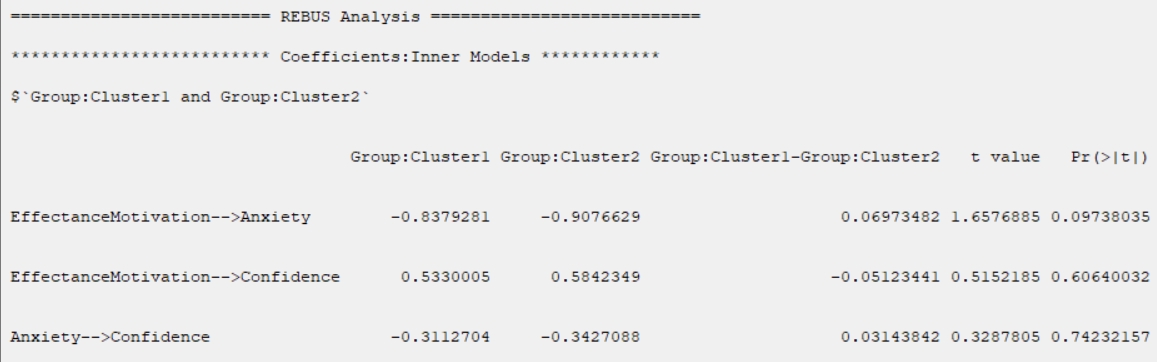
B4. Run Results (t test):
After clicking on the “Run Results” button, for each pair of clusters, you can see the selected test results in
the main software window.
This table compares the inner models coefficients for each of the relationships. In this table, The following indexes are provided:
*The coefficient of each relationship in each cluster
*The coefficient difference between the two clusters
*t value (See
Introduction to SEM-PLS: E.4.3. REBUS (Response Based Unit Segmentation
)
*P-Value as shown in the table with Pr(>|t|). (See
Introduction to SEM-PLS: E.4.3. REBUS (Response Based Unit Segmentation
)
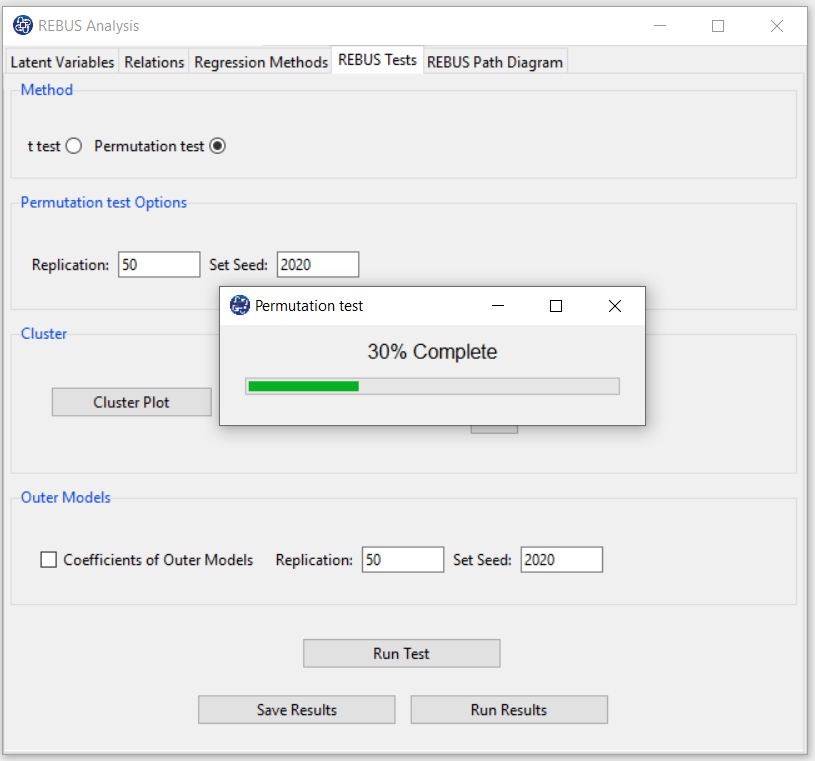
B5. Run Results (Permutation test):
Due to the “Permutation test” structure, this test requires more time than other tests.
The percentage of progress of this test will be determined.
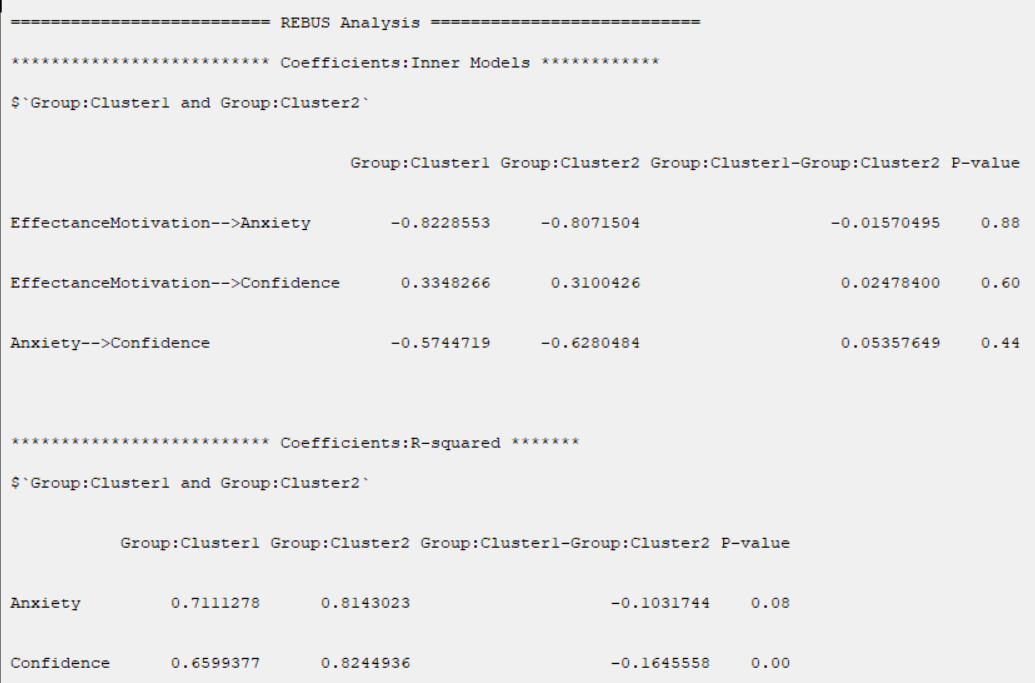
t test can not test the difference between groups in R2, GOF, Cohen's f2, ME, MSE, RMSE, and MAE indices.
The permutation test suggests solving this problem.
In R-squared(R2), RMSE, MAE, ME, these indices are separated by the name of the dependent variable.
C3.1 Permutation test Options:
The permutation test is performed with the following features:
*Replication: Number of Replication(B in equations)
*Set Seed: It is an arbitrary number that will keep the results fixed by holding it fixed.
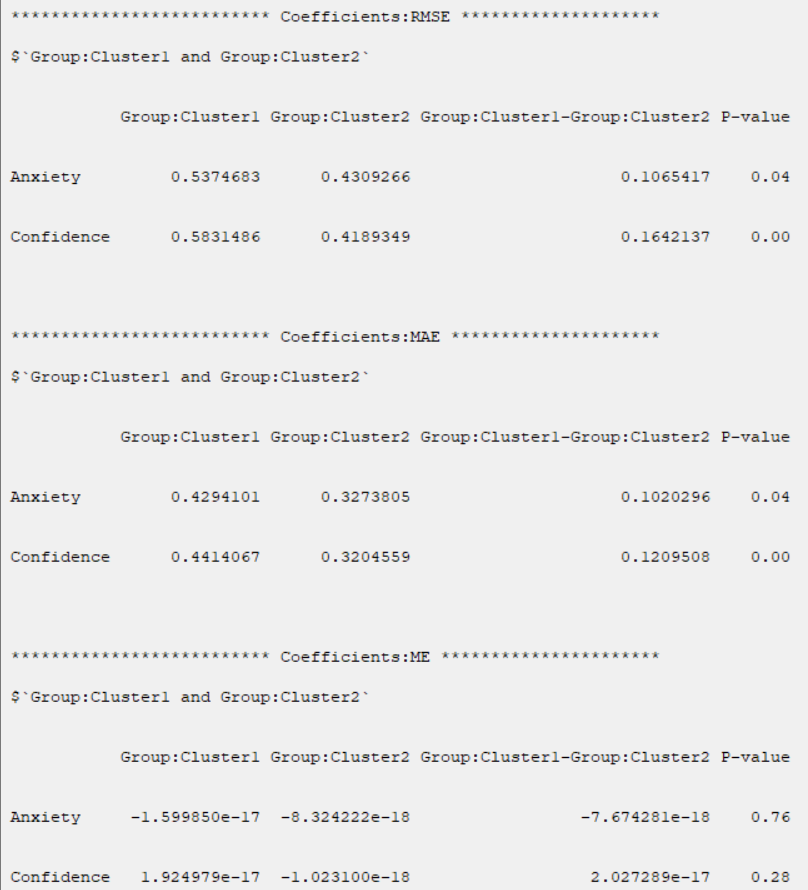
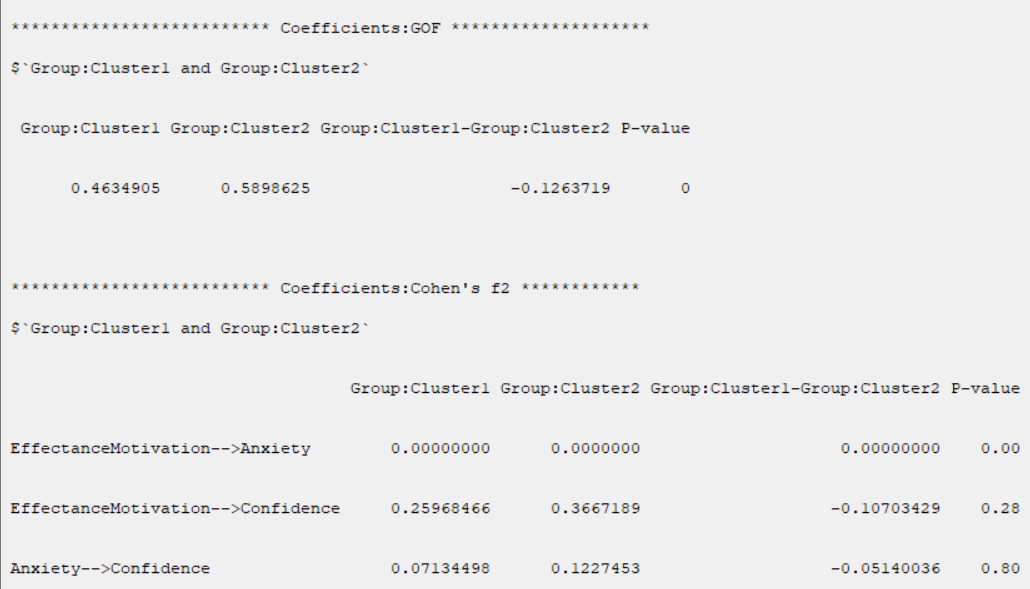
B6. Outer Models (Coefficients of Outer Models):
If you enable this option, you can compare measurement variables in different clusters.
After activating this option, a table with the following title will appear in the results:
“*********Coefficients:Outer Models*****”
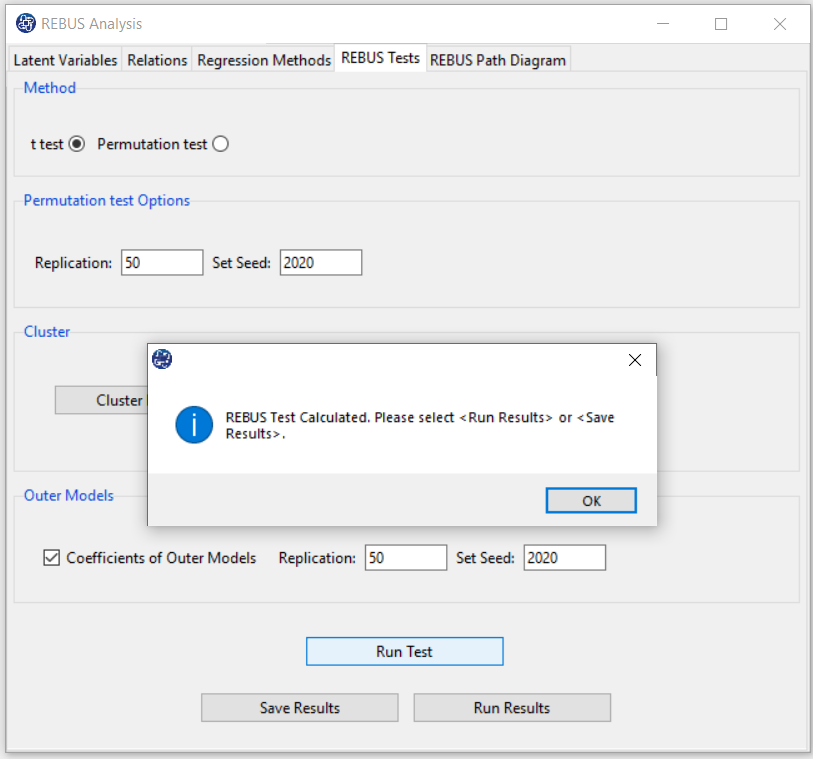
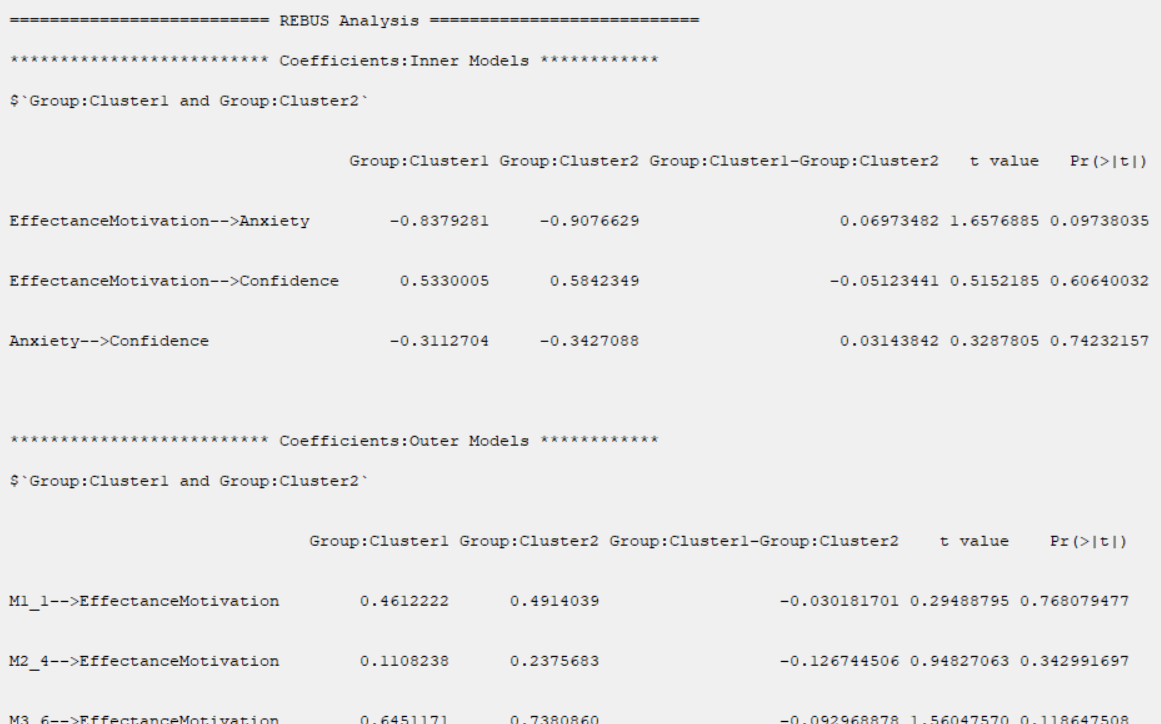
B7. Save Results:
By clicking this button, you can save the REBUS Analysis results. After opening the save results window, you can save the results in “text” or “Microsoft Word” format.
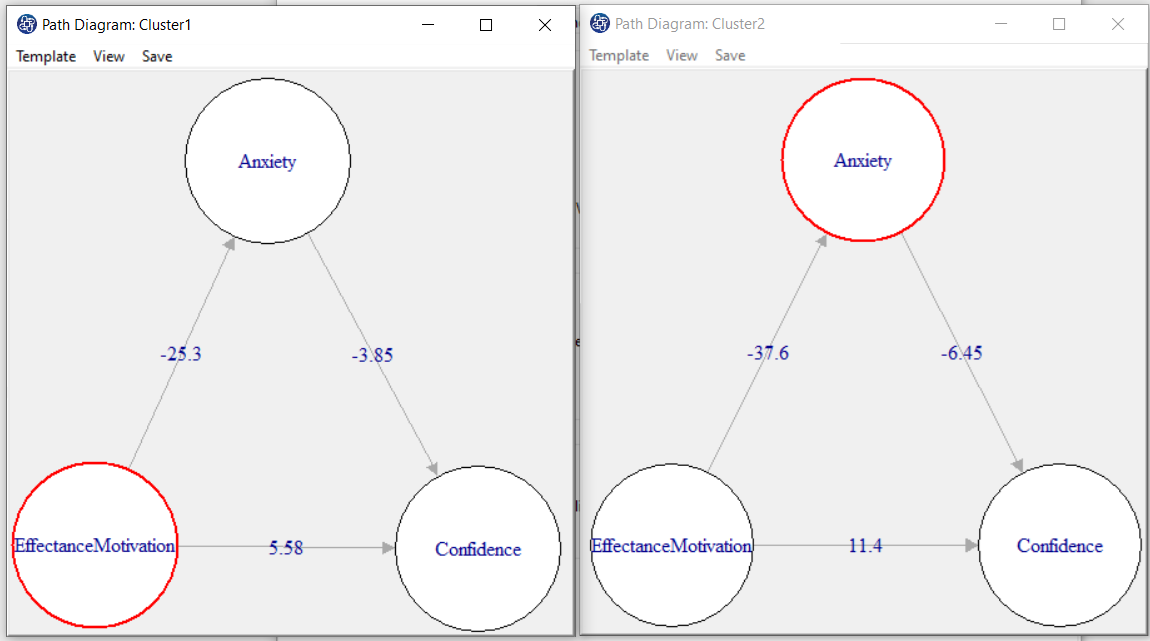
C. REBUS Path Diagram:
This window contains the following three panels:
C1. Type of Plot:
In terms of path coefficient, there are two types of path diagrams:
1-Test Statistic: If this option is enabled, the coefficients in the path diagram will be the value
of the statistic t or F (depending on the regression method). With these coefficients, you can decide whether the relationship between the variables is significant.
2-Factor Loading: If this option is enabled, loadings in the outer model and the coefficients of the
regression in the inner model will appear.
*Plot Measurement Variables: If this option is disabled, only inner models will be the plot.
But if this option is enabled, the outer model will be the plot.
Note: If this option is enabled and we want to plot the path diagram based on the “Test Statistic”,
the results must be executed (“RUN”) by activating the “Outer Models” option.
*Signif. code: By activating this option, the path coefficients(Factor Loading or Test Statistic)
will be displayed with a significant sign.
C2. Cluster:
Based on “Cluster Plot”, you can determine the “Cluster Number” that you want to perform this analysis.
You can increase or decrease the number of clusters with the + or - buttons, respectively.
With the increase (decrease) of the cluster, the number of buttons “Plot Group:Cluter” in the “REBUS Path Diagram” tab will increase (decrease).
C3. Outer Models:
*Coefficients of Outer Models: You can compare measurement variables in different clusters, If you enable this option.
To calculate t value of measurement variables, the software uses the bootstrap method. Bootstrap is performed
with the following features:
*Replication: Number of Replication(B in equations)
*Set Seed: It is an arbitrary number that will keep the results fixed by holding it fixed.
C4. Run:
By clicking on this button, you can estimate the model coefficients by clusters.
Note: If you have performed “Run Test” in the “REBUS Tests” tab, you do not need to run this button to plot a path diagram.
C5. Plot Cluster:
For each cluster, a button for the path diagram will appear. You can examine the effect of this variable by plotting these path diagrams.